Layer 3 cryptos refer to highly scalable and customizable blockchains built on top of layer 2 protocols to host decentralized applications. Let’s explore what is layer 3 crypto, how it enhances blockchain scalability, its use cases and examples.
Summary
Layer 3 cryptos are advanced blockchain protocols that provide extreme scalability, customizability, interoperability and efficiency to decentralized apps (dApps). They solve various limitations of underlying layer 1 blockchain like Ethereum by inheriting security from layer 2 solutions and optimizing for application-specific requirements.
What is a Layer 3 Crypto?
A layer 3 crypto is essentially a tailored blockchain network that emerges out of an existing layer 2 scaling solution. While layer 1 blockchains like Ethereum form the base security layer, layer 2s such as Optimism and Arbitrum enable scalability by handling transactions off-chain.
Layer 3s take this further by allowing developers to launch customizable blockchains for specific dApps needs. These can optimize for use cases like high throughput gaming apps or private DeFi platforms.
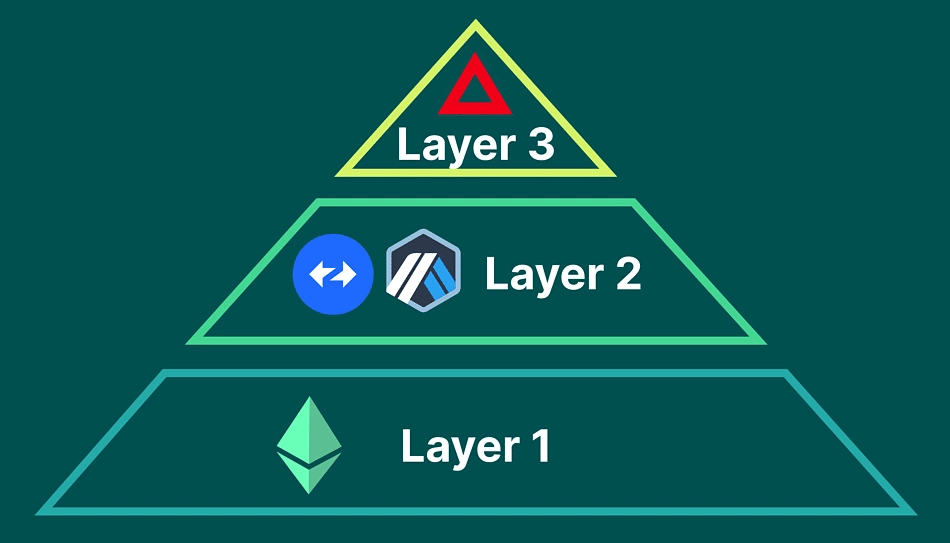
How Do Layer 1s, Layer 2s, and Layer 3s Work Together?
Layer 1 blockchains like Ethereum and Bitcoin form the foundation of the ecosystem by securely settling transactions on-chain. However, they face innate limits to scalability and interoperability.
Layer 2 solutions then build on top of layer 1s to improve transaction throughput and costs by handling operations off-chain while still benefiting from the underlying security.
Finally, layer 3s emerge out of these layer 2 platforms to allow developers to launch customizable blockchains for application-specific needs. These application chains can optimize for use cases ranging from high-throughput DeFi to low-latency gaming apps.
| Layer 1 | Layer 2 | Layer 3 | |
| Role | Decentralized security | Off-chain scaling | Custom app chains |
| Scalability | Low innate limits | Improved from layer 1s | Extremely high |
| Interoperability | Isolated networks | Can bridge a few chains | Application-specific |
| Efficiency | Congestion risks | Reduced fees | Optimized for use case |
| Use Cases | Established currencies | General transactions | Niche dApps needs |
By stacking scalability solutions, blockchain platforms can serve an increasingly diverse array of decentralized applications with varying speed, cost and customization requirements.
What Problems Do Layer 3s Solve?
Layer 3s aim to solve some key limitations in blockchain technology:
Extreme Scalability – Decentralized apps require higher throughput and lower latency than layer 2 rollups can provide today. For example, games need to process tens of thousands of transactions per second. Layer 3s use various optimizations like data sharding and parallelized execution to achieve orders-of-magnitude greater scalability.
Customizability – Developers want better control and flexibility when building their application’s architecture based on its specific requirements. For instance, the ability to select customized governance structures or tweak fee models. Layer 3s allow developers to launch sharded chains with configurable properties.
Enhanced Privacy – Many decentralized apps process sensitive user data related to identity, locations or transactions. Layer 3s enables the creation of permissioned app chains that reveal data only to authorized parties through private transactions and zero-knowledge cryptography.
Bridging Assets – There is an increasing need for interoperability solutions that allow seamless transfers of crypto assets between different layer 1s and layer 2s. Customized layer 3s can become the hub connecting disperate blockchain networks.
Use Cases of Layer 3s
We can expect bespoke layer 3 solutions targeted at certain high-value use cases:
Gaming – By operating on a dedicated gaming chain, developers can offer players low-fee micropayments, near-instant trade marketplaces and lag-free multiplayer experiences that minimize disruptions.
Decentralized Finance – DeFi requires processing high volumes of real-time swap transactions, price oracle updates, liquidations and interest computations. Custom layer 3s allow changing parameters to achieve sub-second finality of such operations.
Enterprises – Organizations demand control over governance for their blockchain network’s access permissions, upgrades, and economics. Layer 3s can enable private chains with such configure-to-order properties.
Cross-Chain Bridging – Chains optimized for asset transfers can connect external layer 1s and 2s. This allows building decentralized exchange functionality and arbitraging price differences between blockchain networks.
Examples of Layer 3s
| Protocol | Highlights |
| Arbitrum Nitro | Configurable chains for permissioning, native tokens, governance rules |
| zkSync Hyperchains | ZK-based chains inherit security of Ethereum |
| Xai Network | Gaming-centric network powered by Arbitrum |
Challenges and Opportunities of Layer 3 Blockchain
While layer 3s usher new possibilities, they also pose challenges around balancing tradeoffs:
Customization vs Interoperability – Highly customized application chains improve utility for that specific use case but reduce seamless interoperability with other networks. Finding the right balance is key.
Scalability vs Decentralization – Layer 3s may sacrifice decentralized security to differing extents in order to achieve hyperscaling. But reduced security also creates vulnerabilities.
Fractionalization Risks – As numerous niche layer 3s emerge, it can create a fragmented ecosystem. This negatively impacts user experience as moving assets across chains becomes complex.
However, if executed judiciously, layer 3s present a major opportunity to significantly expand blockchain’s total addressable market. By allowing custom-fit solutions for specialized needs from gaming to DeFi, mainstream adoption can accelerate.
Future of Layer 3 Blockchain
The future direction of layer 3 platforms remains an open-ended debate. While more experimentation with application-specific chains on layer 2s will likely occur, there are concerns around fractionalization.
Leading thinkers argue that an ecosystem with “layer 3s built on layer 3s” may be untenable. They advocate for finding the optimal tradeoffs when launching new chains rather than maximizing customization.
As layer 2 scaling matures on networks like Ethereum, Polygon and Solana, we expect more tailored layer 3 solutions to emerge selectively. But these will likely be limited to targeted high-value domains like gaming, NFTs and decentralized finance rather than an uncontrolled proliferation.
Conclusion
Layer 3 crypto networks enable the next evolution in blockchain scaling and adoption by allowing any developer to launch customizable chains purpose-built for their application’s needs. As novel layer 2 scaling tech matures, we can expect unique and domain-specific layer 3 solutions to emerge across gaming, DeFi, enterprises and more.
If you found this overview on layer 3 blockchains informative, you may also want to learn more about:
FAQs
What is the difference between layer 2 and 3?
Layer 2s provide generic scalability to underlying blockchains, while layer 3s allow custom-built app chains that can optimize for specific use cases.
Do layer 3s sacrifice decentralization?
Potentially yes, some layer 3s may compromise on decentralized security in order to prioritize scalability or efficiency for their particular application.
Can Bitcoin have layer 3 solutions?
As of now, Bitcoin’s scripting language has limitations that prevent advanced layer 3 development. However, upgrades like Taproot aim to enable similar functionality in the future.




